Trout Lily is a species of spring ephemeral flower native to North America and dwelling in woodland habitats. Trout Lily forms large colonies in moist woodlands and blooms in the early spring. Trout lily blooms in early spring before the trees growing above it develop leaves, this allows it to have unobstructed access to sunlight and also allows it to grow when soil nutrient levels are high. The common name "trout lily" refers to the appearance of its grey to green leaves mottled with brown or grey, which allegedly resemble the colouring of brook trout. The genus name erythros comes from the greek word for "red", a reference to the flower colour of several European species. The species name americanum means "of America".
There is currently no commercial application for trout lily.
Within the realm of rational and holistic medicine, the bulb and the fresh leaves of trout lily have been used in Native American medicine. Trout Lily, when harvested fresh is strongly emetic and are not used internally. The fresh leaves are also antiscrofulatic and emollient and are used as an infusion or stimulating poultice applied to swellings, tumours and scrofulous ulcers. The juice from crushed leaves has been applied to wounds that are not healing. A poultice of the crushed bulbs has been applied to swellings and to help remove splinters. The raw plant, excluding the roots, has been used by native North American young girls to prevent conception.
Please note that MIROFOSS does not suggest in any way that plants should be used in place of proper medical and psychological care. This information is provided here as a reference only.
The bulbs of trout lily can be consumed raw, or cooked, and have a crisp chewy and very pleasant taste. The leaves of the trout lily plant, raw or cooked, can be added to salads. The flowers and flower buds of trout lily are considered to be edible.

Trout lily plants do not flower for the first four to seven years of its life. While the plant it too young to flower it will grow one leaf and once it has reached maturity may grow two paired leaves and a flower stalk. In any given trout lily colony 99% plants will be non-flowering and only have one leaf and 0.5% will have paired leaves and flowers. Each spring the plant will grow either a single or pair of 8cm to 23cm long elliptic to linear leaves, the leaves may be mottled with grey to purple and have entire leaf margins. Yellow trout lily produces an erect flower stalk with nodding one-inch, bisexual yellow flowers with six tepals, the tepals are composed of three petals and three petal-like sepals which are both re-curved upward. The fruit is a capsule 12mm to 15mm long. Trout Lily flowers close at night. Trout lily grows from a corm, or underground bulb 15mm to 28mm long and shaped like an oval. The corm is often located in the upper 11cm of soil although it may be as deep as 30cm. The bulbs of the trout lily plant are buried very deeply compared to other lily family plants. In North America trout lily does not reproduce very effectively via sexual reproduction with only 10% of pollinated flowers developing seeds. In North America, trout lilies grow in colonies that may be up to 300 years old. The individuals within a colony will often reproduce asexually via a "dropper" or from small corms budding off of the main corm. A dropper is a tubular fleshy stem that grows out from a parent corm, up toward the surface and then penetrates deep into the soil where another corm is formed from the tip of the dropper. The stem connecting the daughter and parent corm then dies. Trout lily is a myrmecochorous plant, meaning ants help to disperse the seeds and reduce predation of the seeds. To make the seeds more appealing to ants they have an elaiosome which is a structure which attracts the ants.
| Plant Height |
10cm to 18cm |
| Habitat |
Rich woodlands |
| Leaves |
Elliptic to Linear |
| Leaf Margin |
Entire |
| Leaf Venation |
Parallel |
| Stems |
Smooth Stems |
| Flowering Season |
March to June |
| Flower Type |
Radially Symmetrical |
| Flower Colour |
White |
| Pollination |
Bees, Insects |
| Flower Gender |
Flowers are hermaphrodite and the plants are self-fertile |
| Fruit |
Hard kidney shaped seeds |
| USDA Zone |
4B (-28°C to -31°C) cold weather limit |
The following health hazards should be noted when handling or choosing a location to plant trout lily:
 |
Note
Although no records of toxicity have been seen for this species, the following notes have been seen for another member of this genus and so some caution is advised. Skin contact with the bulbs has been known to cause dermatitis in sensitive people.
|
 |
-Click here- or on the thumbnail image to see an artist rendering, from The United States Department of Agriculture, of trout lily. (This image will open in a new browser tab) |
 |
-Click here- or on the thumbnail image to see a magnified view, from The United States Department of Agriculture, of the seeds created by trout lily for propagation. (This image will open in a new browser tab) |
Trout Lily can be referenced in certain current and historical texts under the following two names:
Trout Lily can be translated into the following select languages: |
| Arabic |
سمك السلمون المرقط الزنبق |
Bulgarian |
Пъстърва Лили |
Chinese (Sim) |
鳟鱼百合 |
| Croatian |
|
Czech |
|
Danish |
|
| Dutch |
Lelie van de forel |
Esperanto |
|
Estonian |
|
| Finnish |
|
French |
|
German |
|
| Greek |
|
Hebrew |
טראוט לילי |
Hungarian |
|
| Italian |
|
Japanese |
トラウトリリー |
Korean |
송어 릴리 |
| Punjabi |
|
Lithuanian |
upėtakis Lelija |
Norwegian |
|
| Persian |
ماهی قزل آلا لیلی |
Polish |
|
Portuguese |
|
| Romanian |
|
Russian |
|
Slovak |
|
| Spanish |
lirio de trucha |
Swedish |
|
Tagalog |
|
| Turkish |
bahar güzelliği |
Ukrainian |
|
Vietnamese |
|
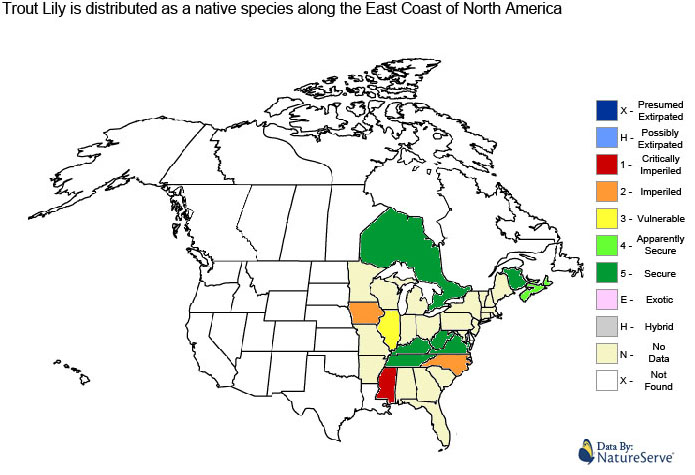
The information provided in this conservation assessment has been provided by the Natureserve Database in conjunction with various federal, provincial, state, county, district, regional, and municipal governments as well as public and private conservation authorities. Information in this section is accurate from the last time this article was updated.
|
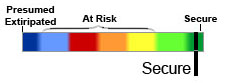 |
Trout Lily is considered to be a secure native species in North America. |
 |
The MIROFOSS database offers free printable garden tags for personal and non-profit use. These tags can be used to properly identify plant samples in a garden. Click on the tags shown on the the screen or -click here- to download a full size jpeg image for a trout lily identification tag; which can be printed on paper or used with a plastic laser printer. |
 |
What's this?
This is a QR code (short for Quick Response) which gives fast-track access to MIROFOSS articles. QR Codes are barcodes that can be read by smart phone cameras. This QR Code is unique to this MIROFOSS article.
What can I do with it?
You can copy and print the QR code to a plant label, poster, book, web site, magazines, or newspaper so smart phone users can scan the QR Code which automatically takes them to this specific article. |

| Description |
Bernhardt, Peter (2003). Wily violets & underground orchids : revelations of a botanist (University of Chicago Press ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 9780226043661 |
| Description |
Muller, Robert (1978). "THE PHENOLOGY, GROWTH AND ECOSYSTEM DYNAMICS OF ER YTHRONIUM AMERICANUM IN THE NORTHERN HARDWOOD FOREST". Ecological monographs (48): 1–20. |
| Commercial Uses |
Kartesz, J.T. 1994. A synonymized checklist of the vascular flora of the United States, Canada, and Greenland. 2nd edition. 2 vols. Timber Press, Portland, OR. |
| Distribution |
Flora of North America Editorial Committee. 2002a. Flora of North America North of Mexico. Vol. 26. Magnoliophyta: Liliidae: Liliales and Orchidales. Oxford Univ. Press, New York. xxvi + 723 pp. |
| Biology |
Dickinson, T.; Metsger, D.; Bull, J.; & Dickinson, R. (2004) ROM Field Guide to Wildflowers of Ontario. Toronto:Royal Ontario Museum, |
| Image Rendering |
USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / USDA NRCS. Wetland flora: Field office illustrated guide to plant species. USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. |
| Environment |
National Audubon Society. Field Guide To Wildflowers (Eastern Region): Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 0-375-40232-2 |
| Physical Identification |
National Audubon Society. Field Guide To Wildflowers (Eastern Region): Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 0-375-40232-2 |
| August 27, 2016 |
The last time this page was updated |
| ©2021 MIROFOSS™ Foundation |
 |
|
|