![]()
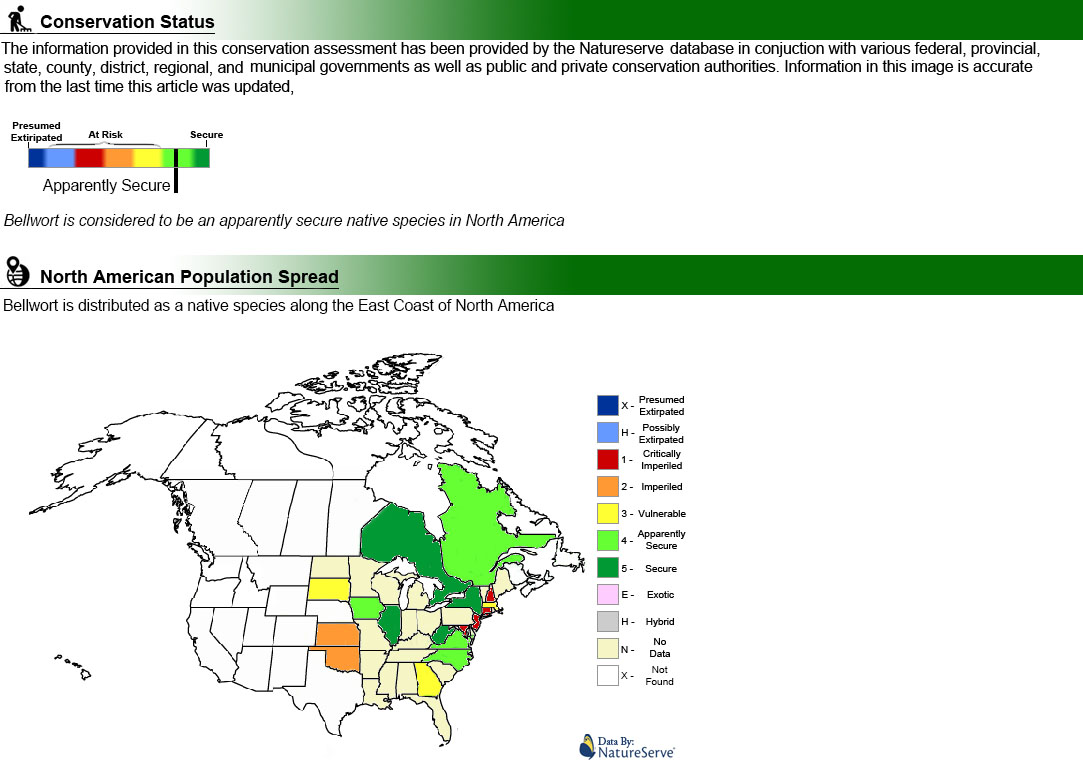
Bellwort is a perennial flower in the colchicum family which is native to Eastern North America. One of the first wildflowers to grow and bloom; bellwort can be distinguished by it's large drooping yellow flowers. The genus name comes from the Latin word 'uvula', which references the hanging structure at the back of the human throat; which shares visual similarity to the bellwort flower. The species name 'grandiflora' means large flowered.
![]()
Bellwort is grown and solid as an ornamental plant.
![]() Within the realm of rational and holistic medicine, bellwort root is used as an analgesic. The root is ground and used as a poultice or salve in the treatment of toothaches, boils, swellings, wounds and ulcers. An infusion of the root has been used to treat backaches and, mixed with oil, has been used as a salve on sore muscles. A tea made from the roots is used as a wash in the treatment of rheumatic pains.
Within the realm of rational and holistic medicine, bellwort root is used as an analgesic. The root is ground and used as a poultice or salve in the treatment of toothaches, boils, swellings, wounds and ulcers. An infusion of the root has been used to treat backaches and, mixed with oil, has been used as a salve on sore muscles. A tea made from the roots is used as a wash in the treatment of rheumatic pains.
Please note that MIROFOSS does not suggest in any way that plants should be used in place of proper medical and psychological care. This information is provided here as a reference only.
![]()
There is currently no edibility information about bellwort.
![]()
Bellwort can grow in light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: acid, neutral and basic (alkaline) soils. It can grow in full shade (deep woodland) or semi-shade (light woodland). It prefers moist soil. Bellwort is known to attract insects and butterflies.
| Soil Conditions | |
| Soil Moisture | |
| Sunlight | |
| Notes: |
![]()
Bellwort plants can reach a height of up to 75cm, and a clump width of 30cm across. The leaves of the bellwort plant are ovate or oblong shape and arranged alternately along the stem of the plant. Each leave can be 6cm to 13cm long and 2cm to 7cm wide. The leaves are smooth on the top side and small hairs on the undersides. The flowers are yellow in colour, 10mm to 30mm long, and droop from the stems of the plant. Each flower has three petals, three sepals, three stamens, and six pistils. In late summer three capsuled ovaries split open releasing seeds that have attached food bodies called elaiosom which are attractive to ants that collect and redistribution the seeds.
![]()
| Plant Height | 75cm | 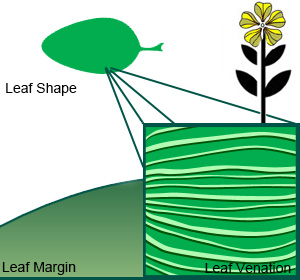 |
| Habitat | Rich moist woods | |
| Leaves | Ovate | |
| Leaf Margin | Entire | |
| Leaf Venation | Parallel | |
| Stems | Smooth Stems | |
| Flowering Season | April to June | |
| Flower Type | Radially Symmetrical | |
| Flower Colour | Yellow | |
| Pollination | Bees, Insects | |
| Flower Gender | Flowers are hermaphrodite and the plants are self-fertile | |
| Fruit | Hard round seeds | |
| USDA Zone | 4A (-31°C to -34°C) cold weather limit |
![]()
No known health risks have been associated with bellwort. However ingestion of naturally occurring plants without proper identification is not recommended.
![]()
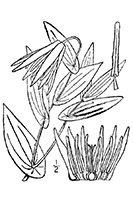 |
-Click here- or on the thumbnail image to see an artist rendering, from The United States Department of Agriculture, of bellwort. (This image will open in a new browser tab) |
![]()
 |
-Click here- or on the thumbnail image to see a magnified view, from BotanyCa, of the seeds created by bellwort for propagation. (This image will open in a new browser tab) |
![]()
Bellwort can be referenced in certain current and historical texts under the following three names:
Bellwort can be translated into the following select languages:
| Arabic | Bulgarian | Chinese (Sim) | |||
| Croatian | Czech | Danish | |||
| Dutch | Esperanto | sonorilo | Estonian | ||
| Finnish | French | German | |||
| Greek | Hebrew | פעמון | Hungarian | ||
| Italian | Japanese | キンギョソウ | Korean | 종다리 | |
| Punjabi | ਬੈਲਵਾਲਟ | Lithuanian | varpinė | Norwegian | |
| Persian | زنگ زدن | Polish | Portuguese | candelária de bexiga | |
| Romanian | Russian | Slovak | |||
| Spanish | campana | Swedish | Tagalog | kampanilya | |
| Turkish | Ukrainian | Vietnamese | quả chuông |
![]()
 |
The MIROFOSS database offers free printable garden tags for personal and non-profit use. These tags can be used to properly identify plant samples in a garden. Click on the tags shown on the the screen or -click here- to download a full size jpeg image for a bladder campion identification tag; which can be printed on paper or used with a plastic laser printer. |
 |
What's this? What can I do with it? |
![]()
| Description | RHS A-Z encyclopedia of garden plants. United Kingdom: Dorling Kindersley. 2008. p. 1136. ISBN 1405332964. |
| Description | Timothy P. Spira (16 May 2011). Wildflowers and Plant Communities of the Southern Appalachian Mountains and Piedmont: A Naturalist's Guide to the Carolinas, Virginia, Tennessee, and Georgia. Univ of North Carolina Press. pp. 462–. ISBN 978-0-8078-7765-4. |
| Description | Charlotte Adelman; Bernard L. Schwartz (21 September 2011). The Midwestern Native Garden: Native Alternatives to Nonnative Flowers and Plants. Ohio University Press. pp. 77–. ISBN 978-0-8214-4356-9. |
| Folklore | Smith, Huron H. (1933). "Ethnobotany of the Forest Potawatomi Indians". Bulletin of the Public Museum of the City of Milwaukee. 7: 56, 57, 64. |
| Biology | Dickinson, T.; Metsger, D.; Bull, J.; & Dickinson, R. (2004) ROM Field Guide to Wildflowers of Ontario. Toronto:Royal Ontario Museum, |
| Image Rendering | USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / USDA NRCS. Wetland flora: Field office illustrated guide to plant species. USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. |
| Environment | National Audubon Society. Field Guide To Wildflowers (Eastern Region): Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 0-375-40232-2 |
| Physical Identification | National Audubon Society. Field Guide To Wildflowers (Eastern Region): Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 0-375-40232-2 |
| March 13, 2019 | The last time this page was updated |
| ©2021 MIROFOSS™ Foundation | |
 |
|








